O To ensure the smooth and safe running of trains o To achieve maximum speeds o To carry heavy axle loads o To avoid accidents and derailments due to a defective permanent way o To ensure. In the case of reconstruction the railway track follows the original body and only improves certain elements of the track but in the case of modernization eg.
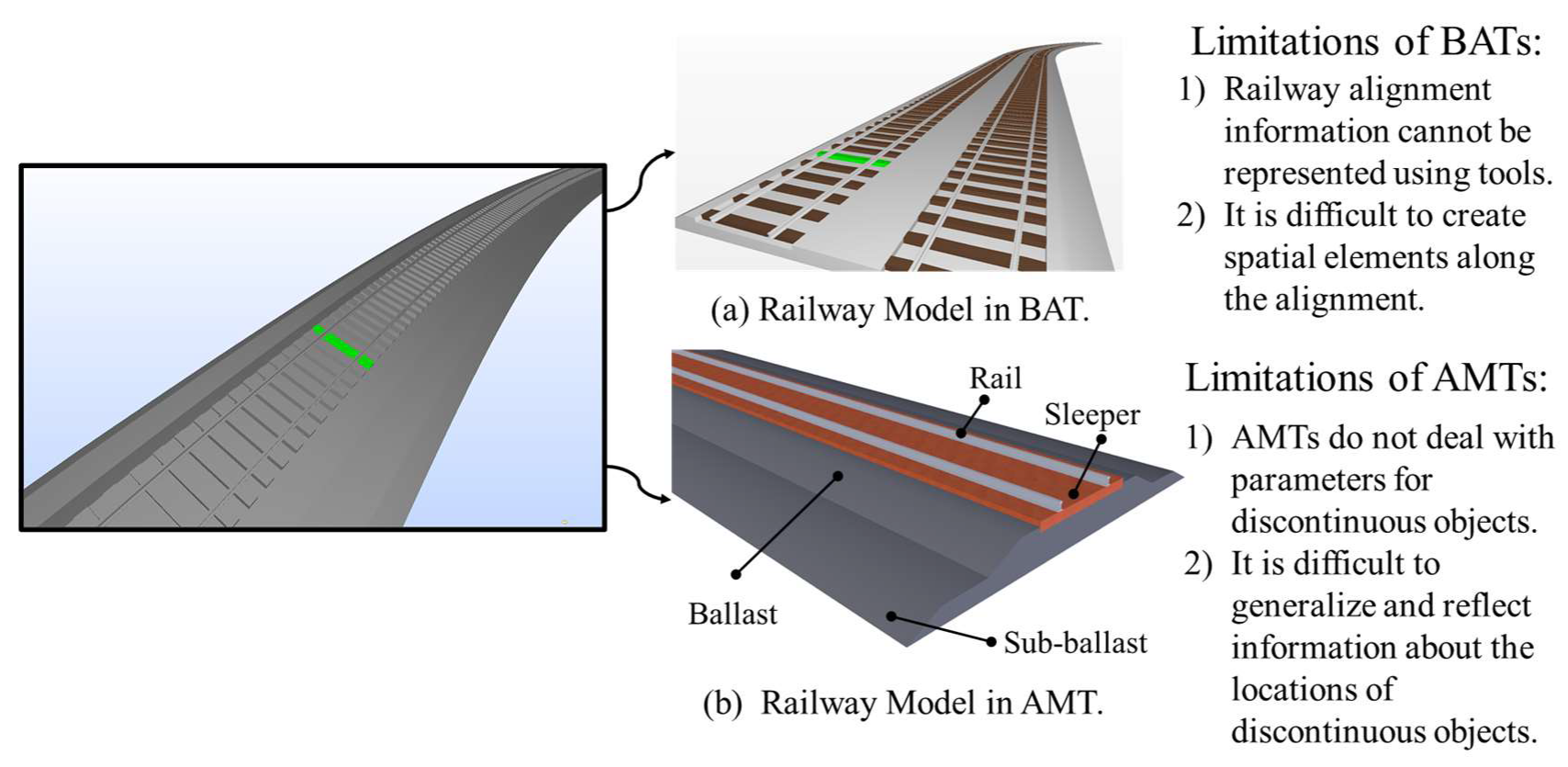
Applied Sciences Free Full Text Design Of Railway Track Model With Three Dimensional Alignment Based On Extended Industry Foundation Classes Html
This leaves the contractors with the task to design.
. Resistance to traction 13. Provides for passenger comfort. The speed and axle load of the train are very important and sometimes are also included as parameters to be considered while arriving at the geometric design of the track.
The distance between the rails. This standard specifies the track geometry requirements for the design and construction of rail track on the AMPRN train system. A numerical or measurable factor forming one of a set that defines a system or sets the conditions of its operation.
Alignment horizontal curves super elevation equilibrium cant and cant deficiency Length of transition curves Gradients and grade compensation vertical curves. Trains can roll safely down 03 grade without wasting energy on brakes. Airport Planning design by SKKhanna MG.
Railway track gauges 3. 2 and in October 2012 Track No. Other Tie 1435 m Rail Rail Ballast Subgrade FIGURE 45 Railroad track geometric cross section.
In the case of geometric design the very first thing which we are going to discuss is alignment of the track. Track fittings 11. Curvature of the track including horizontal and vertical curves transition.
Geometric Design of Railway Track. Earthwork and drainage for railway track 9. B For non-Transition curve.
Geometric design of railway track pdf. In one of the versions when varnishing the nail plate the opening remains uncovered. Railway cross sections are as shown in Figure 45.
For V 160 kmh the track route usually leaves the original body in some sections of the new railway track as there is the axis alignment of the route under ŽSR Z10. Railway engineering nptel pdf. Railway stations and yards.
V080 speed calculated in a c For high speed Trains V458R. This handbook is meant to elucidate these areas of track geometry design. Geometric Design of The Track.
Railway engineering notes pdf downloadgeometric design of railway track notes. Arora SSJain- Nemchand Bros. Surveys and alignment of railway lines 4.
Track section with unconventional construction of railway superstructure called slab track ST was put in operation in July 2012 track No. Geometric Design Geometric design for transportation facilities includes the design of geometric cross. CEE 411 3 Geometric Design Superelevated Spiral Curves Most railway curves use superelevation and spiral transitions Actual superelevation E a is inches of elevation difference between high rail outside and low rail inside on a curve Typical maximum value for E a on freight lines is 4 inches Track is rotated about the low rail in curves Unlike highways which.
At first the basic principles of track geometry design and related subjects are discussed. Curves of the track including horizontal and vertical curves transition curves sharpness of curve in terms of radius or degree of the. There are also many variants of the moon manicure.
For the track RP6 V max 250 kmh according to Standard 3 supplemented by Standard 1 p max 150. For light rail transit main line tracks the absolute minimum length of the vertical curve depends on the design speed of the track and the algebraic difference of the grades connected by the curve. Necessity 21 Necessity The need for proper geometric design of a track arises because of the following considerations.
Railway traction 5. Necessity 21 Necessity The need for proper geometric design of a track arises because of the following considerations. In another variation of the nail design the opening is stained with a different color.
Any departure of track from the level is known as grade or gradient. Now in the case of this lecture the The course introduces various modes of transportation systems like railways Airways. Fehr Member NMRA RP-12 Turnout Working Group.
Geometric Desing of Railway Track Page 6 Chapter 2. L D R. Recommended criteria are given in the Track Design Handbook for Light Rail Transit for the desired length the.
Railway track - dynamic solution design in 3D. Ii For NG V 365R-6 For V is kmhr. Geometric Desing of Railway Track Page 6 Chapter 2.
The classical railway track basically consists of a flat framework made up of rails and sleepers which is supported on ballast. Ban31881_ch04qxd 61401 907 AM Page 65. Safe speed Based on Super Elevation.
A reliable and robust railway track geometry is one of the most important feature of a dependable railway track systems. Geometric design should be such as to provide maximum efficiency in the traffic operation with maximum safety at reasonable cost. Engineering Analysis and Geometric Design of Model Railroad Turnouts NMRA Technical Note TN-12 By.
V4355-67 where V is in kmph. GEOMETRIC DESIGN OF TRACK Geometric design of railway track includes all those parameters which effect the geometry of the track. Defines track geometry limits for construction.
Figure 81 and Figure 82 show the construction principle of the classical track struc- ture. Gradients in the track including grade compensation rising gradient and falling gradient. REES Module 6 - Railway Alignment Design and Geometry 14 Design Grade for Railways Ideal maximum for railway grade.
Basic and sweet All of this manicure requires is a couple of techniques. O To ensure the smooth and safe running of trains o To achieve maximum speeds o To carry heavy axle loads o To avoid accidents and derailments due to a defective permanent way o To ensure that the. Track geometry degrades with age and usage.
This necessitates development and implementation of an applicable and cost-effective. In the second part the elements of. Points and crossings 14.
66 CHAPTER 4. CE2303 Railway Engineering Introduction Parameters determines or affect geometry of the track Gradient Speed Super-elevation etc. Also the use of geodetic co-ordinates are explained.
Track section is part of double-track modernized railway track Nove Mesto nad Vahom Puchov and is situated in the tunnel Turecky vrch and around its portals. Railway Track Engineering Tata McGraw Hill Book Co. The ballast bed rests on a sub-ballast layer which forms the transition layer to the formation.
And loses its functionality over time. Track height line and track tilt in curves. Safe speed on curves Based on Martins Formula a For Transition curve i For B G MG.
These include for example the track centre line. Defines track geometry parameters used in design of new track and rating of existing track. Purpose of providing gradient.
Gradient in the track including grade compensation rising gradient and falling gradient. Geometric design of a track 12. Under revision.
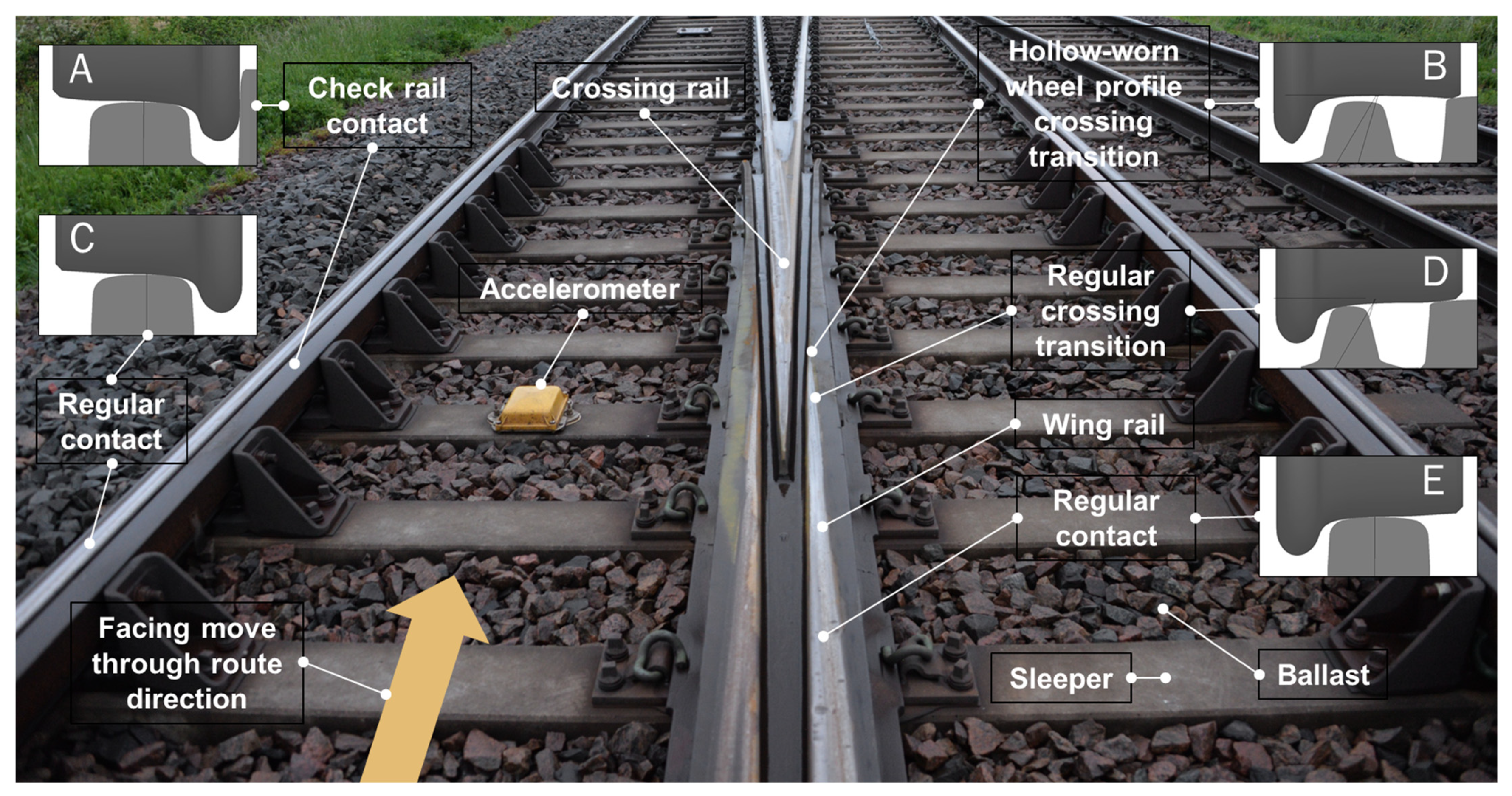
Sensors Free Full Text Condition Monitoring Of Railway Crossing Geometry Via Measured And Simulated Track Responses Html

Schematic Of The Two Layer Three Dimensional Track System Model Download Scientific Diagram

Uic S Track Structures Sector Publishes First Edition Of Irs 70719 Earthworks And Track Bed Layers For Railway Lines Design And Construction Principles Uic Communications
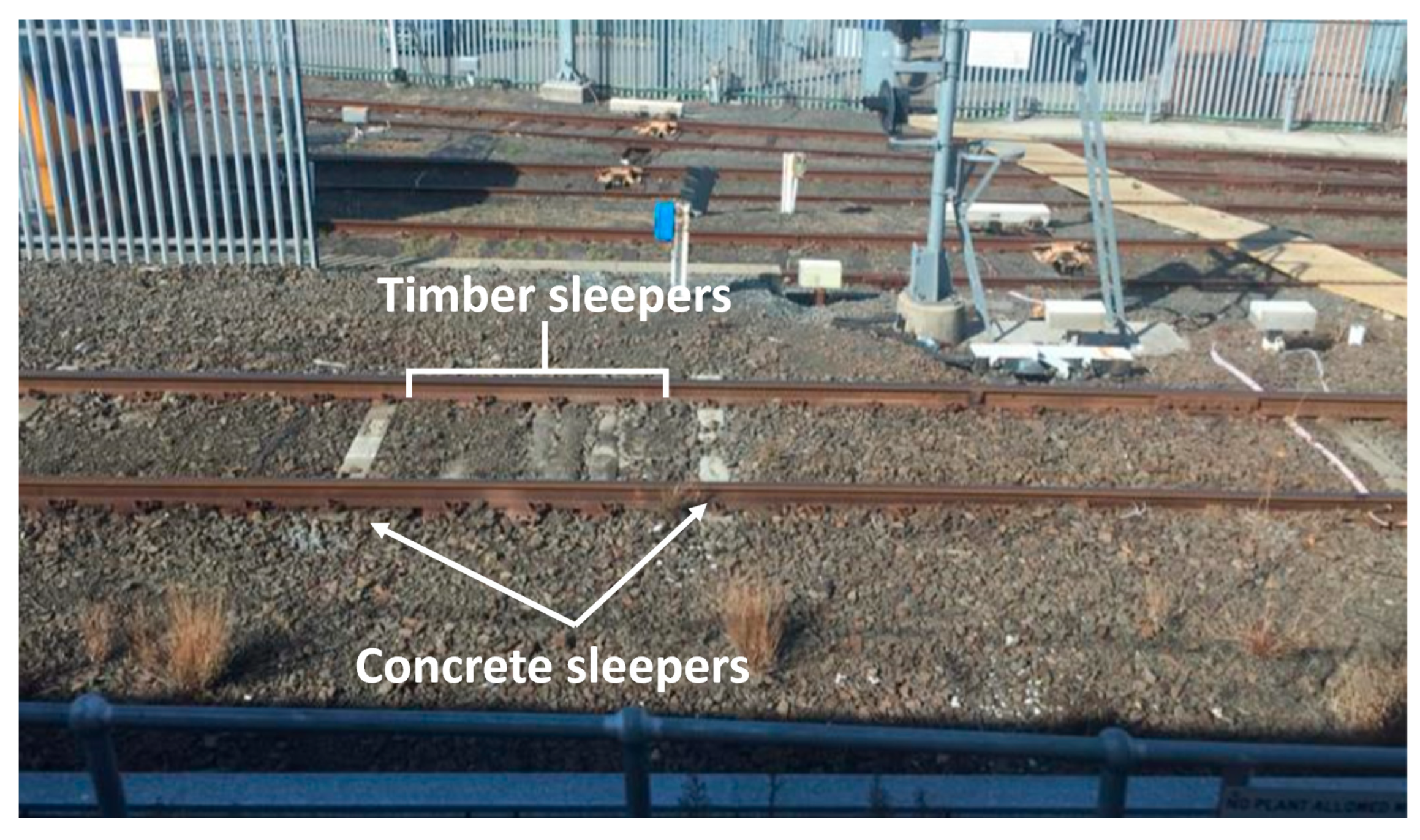

Applied Sciences Free Full Text Buckling Analysis Of Interspersed Railway Tracks Html

Typical Components Of A Railway Turnout Download Scientific Diagram

Typical Ballasted Railway Tracks From D Track 1 Download Scientific Diagram

0 comments
Post a Comment